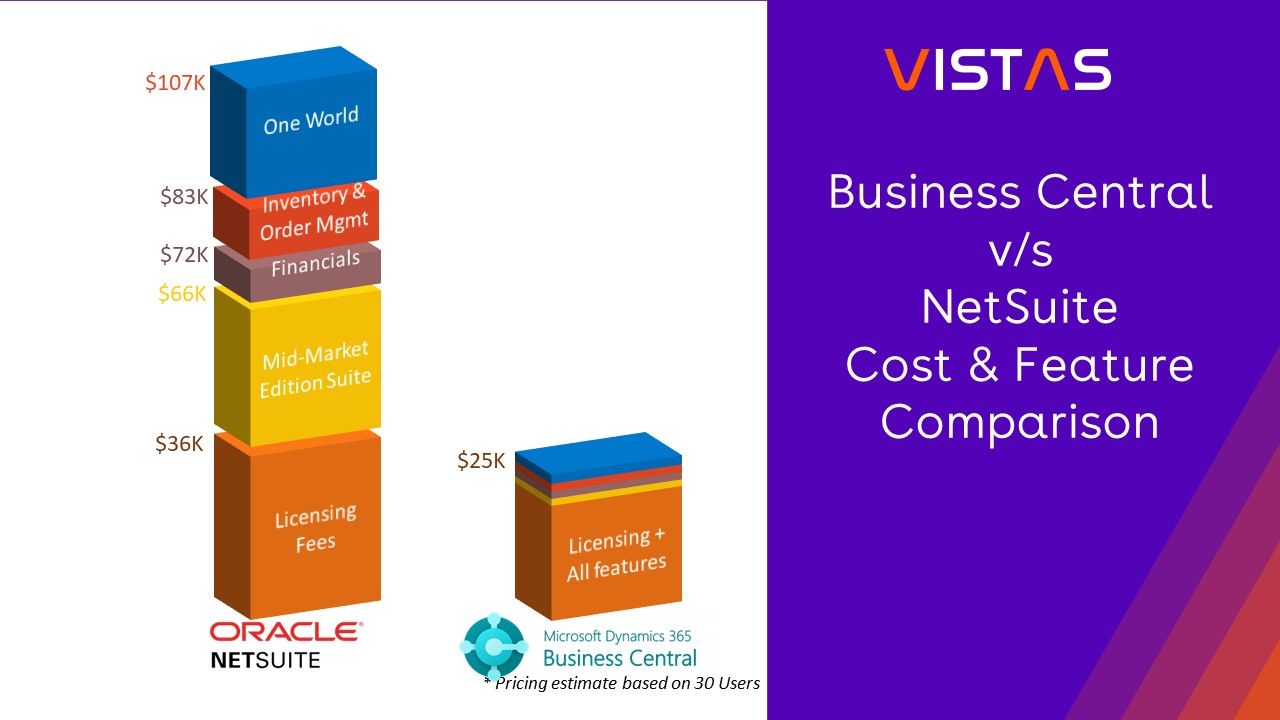
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Overview Series - Make Manufacturing Easy
Manufacturing is the backbone of the nation and economy. The United States stands behind China at second in manufacturing while India is in sixth place. Now you can imagine how important is manufacturing to a country and the world economy. Manufacturing is defined as producing goods through labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the secondary sector of the economy. Manufacturing refers to a range of human activities, from handicraft to high-tech. In industrial design, raw materials from the primary industry are transformed into finished goods on a large scale. Such goods may be sold to other manufacturers to produce complex products (such as aircraft, household appliances, furniture, sports equipment, or automobiles) furthermore or distributed via the tertiary industry to end-users and consumers. Manufacturing engineering, or the manufacturing process, is the steps through which raw materials are transformed into a final product. The manufacturing process begins with the product design and materials specification from which the product is made. These materials are then modified through manufacturing processes to become the required part.
Methods of Manufacturing
- Agile manufacturing
Agile manufacturing is an approach to manufacturing that is focused on meeting the needs of customers while maintaining high standards of quality and controlling the overall costs involved in the production of a product. This approach is geared towards companies working in a highly competitive environment, where small variations in performance and product delivery can make a huge difference in the long term to a company’s survival and reputation among consumers.
- Flexible manufacturing
A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react in case of changes, whether predicted or unpredicted.
This flexibility is generally considered to fall into two categories, which both contain numerous subcategories. The first category is called Routing Flexibility which covers the system’s ability to be changed to produce new product types and ability to change the order of operations executed on a part. The second category is called Machine Flexibility which consists of the ability to use multiple machines to perform the same operation on a part, as well as the system’s ability to absorb large-scale changes, such as in volume, capacity, or capability.
- Just-in-time manufacturing
Lean manufacturing (also known as lean production, just-in-time manufacturing, and just-in-time production, or JIT) is a production method aimed primarily at reducing times within the production system as well as response times from suppliers and to customers. Companies employ the strategy to increase efficiency. By receiving goods only as they need them for the production process, it reduces inventory costs and wastage and increases productivity and profit. The downside is that it requires producers to forecast demand accurately as the benefits can be nullified by minor delays in the supply chain. It may also impact negatively on workers due to added stress and inflexible conditions. A successful operation depends on a company having regular outputs, high-quality processes, and reliable suppliers.
- Reconfigurable manufacturing
A reconfigurable manufacturing system (RMS) is one designed at the outset for rapid change in its structure, as well as its hardware and software components, to quickly adjust its production capacity and functionality within a part family in response to sudden market changes or intrinsic system change. Ideal reconfigurable manufacturing systems possess six core RMS characteristics: modularity, integrability, customized flexibility, scalability, convertibility, and diagnosable. A typical RMS will have several of these characteristics, though not necessarily all. When possessing these characteristics, RMS increases the speed of responsiveness of manufacturing systems to unpredicted events, such as sudden market demand changes or unexpected machine failures. The RMS facilitates a quick production launch of new products and allows for adjustment of production quantities that might unexpectedly vary. The ideal reconfigurable system provides exactly the functionality and production capacity needed and can be economically adjusted precisely when needed.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Manufacturing functions:
Manufacturing systems are part of supply chain execution suites, or modules of an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system like Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central. Depending on the size and sophistication of the company, manufacturing can be automated through Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central -software systems.
- Assembly Management
Specify a list of sellable the items, raw materials, subassemblies, and resources as an assembly bill of materials that make up a finished item or a kit. Use assembly orders to replenish assembly items. Capture customer requirements for the kit’s bill of materials directly from sales quotes, blanket orders, and order lines in the assembly-to-order processes.
- Standard Cost Worksheet
Give company controllers a reliable and efficient way to maintain accurate inventory costs. Work with standard cost updates in Business Central in the same way you would in an Excel spreadsheet. Prepare for cost updates without changing data until you’re ready.
- Production Bill of Materials
Create bills of materials and calculate their standard costs.
- Basic Capacity Planning
Add capacities (work centers) to the manufacturing process. Set up routings for production orders and material requirements planning. View loads and the task list for the capacities.
- Machine Centers
Add machine centers as capacities in the manufacturing process. Manage capacity for each machine or production resource on a detailed level for machine centers, and on a consolidated level for work centers. Use machine centers to store default information about manufacturing processes, such as setup times and default scrap percentages.
- Version Management
Create versions of manufacturing bills of materials and routings.
- Production Orders
Create production orders and post consumption and output. Calculate net requirements based on production orders. Use a manual supply planning tool as an alternative to automatic planning. Get visibility and tools to manually plan for demand from sales lines and to create supply orders.
- Finite Loading
Manage finite loading of capacity-constraint resources. Account for capacity constraints for periods to avoid overloading work centers. Calculate capable-to-promise (CTP).
As companies look for innovative ways to respond to changing customer demands, manufacturing is the critical infrastructure for a company and economy. Microsoft Dynamics 365 business central provides a handy approach to deal with manufacturing needs like automation and service needs through an integrated business support system. Microsoft Dynamics 365 business central is a cloud business application supported through a network of partners like VISTAS CLOUD. At VISTAS, we have over a decade of experience serving small to medium-size businesses with all business needs, including manufacturing. We support the unique needs of companies and have the expertise to customize Microsoft Dynamics 365 business central to fit your specific needs.
References
- Walker, William (1993). “National Innovation Systems: Britain”. In Nelson, Richard R. (ed.). National innovation systems: a comparative analysis. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0195076176. Archived from the original on 2021-04-01. Retrieved 2020-11-16.
- Manufacturing & Investment Around The World: An International Survey Of Factors Affecting Growth & Performance, ISR Publications/Google Books, revised second edition, 2002. ISBN 978-0-906321-25-6.
- Research, Industrial Systems (2002-05-20). Manufacturing and Investment Around the World: An International Survey of Factors Affecting Growth and Performance. ISBN 978-0-906321-25-6. Archived from the original on 2021-04-01. Retrieved 2015-11-19.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Capability Guide: by www.microsoft.com
Next: Level-up your Sales Reports with Dynamics 365 Business Central